Bert文本分类实践(一):实现一个简单的分类模型
写在前面
文本分类是nlp中一个非常重要的任务,也是非常适合入坑nlp的第一个完整项目。虽然文本分类看似简单,但里面的门道好多好多,作者水平有限,只能将平时用到的方法和trick在此做个记录和分享,希望大家看过都能有所收获,享受编程的乐趣。
第一部分
模型
Bert模型是Google在2018年10月发布的语言表示模型,一经问世在NLP领域横扫了11项任务的最优结果,可谓风头一时无二。有关于Bert中transformer的模型细节,推荐看这篇。在此不做赘述。
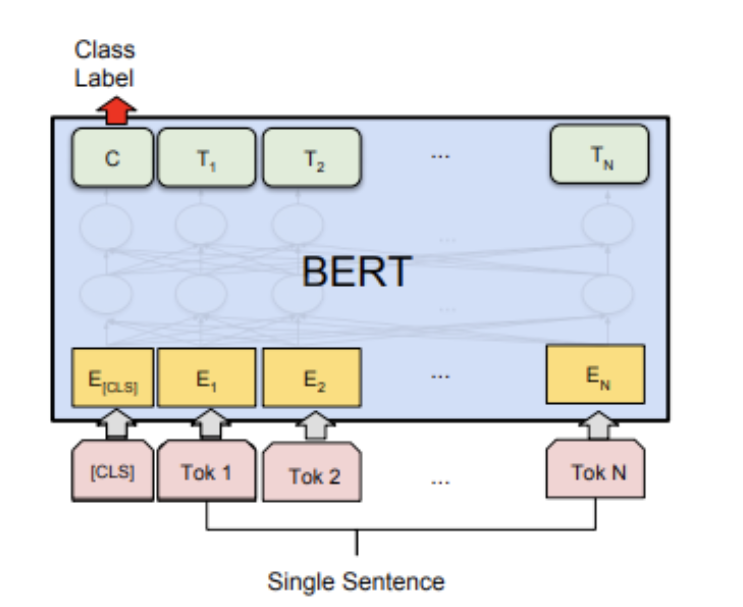
Bert文本分类模型常见做法为将bert最后一层输出的第一个token位置(CLS位置)当作句子的表示,后接全连接层进行分类。模型很简单,我们直接看代码!
第二部分
pytorch代码实现
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# bert文本分类baseline模型# model: bert# date: 2021.10.10 10:01import osimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.utils.data as Dataimport torch.optim as optimimport transformersfrom transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizerimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
train_curve = []
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')# 定义一些参数,模型选择了最基础的bert中文模型batch_size = 2epoches = 100model = "bert-base-chinese"hidden_size = 768n_class = 2maxlen = 8# data,构造一些训练数据sentences = ["我喜欢打篮球", "这个相机很好看", "今天玩的特别开心", "我不喜欢你", "太糟糕了", "真是件令人伤心的事情"]
labels = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0] # 1积极, 0消极.# word_list = ' '.join(sentences).split()# word_list = list(set(word_list))# word_dict = {w: i for i, w in enumerate(word_list)}# num_dict = {i: w for w, i in word_dict.items()}# vocab_size = len(word_list)# 将数据构造成bert的输入格式# inputs_ids: token的字典编码# attention_mask:长度与inputs_ids一致,真实长度的位置填充1,padding位置填充0# token_type_ids: 第一个句子填充0,第二个句子句子填充1class MyDataset(Data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, sentences, labels=None, with_labels=True,):
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model)
self.with_labels = with_labels
self.sentences = sentences
self.labels = labels def __len__(self):
return len(sentences) def __getitem__(self, index):
# Selecting sentence1 and sentence2 at the specified index in the data frame
sent = self.sentences[index] # Tokenize the pair of sentences to get token ids, attention masks and token type ids
encoded_pair = self.tokenizer(sent,
padding='max_length', # Pad to max_length
truncation=True, # Truncate to max_length
max_length=maxlen,
return_tensors='pt') # Return torch.Tensor objects
token_ids = encoded_pair['input_ids'].squeeze(0) # tensor of token ids
attn_masks = encoded_pair['attention_mask'].squeeze(0) # binary tensor with "0" for padded values and "1" for the other values
token_type_ids = encoded_pair['token_type_ids'].squeeze(0) # binary tensor with "0" for the 1st sentence tokens & "1" for the 2nd sentence tokens
if self.with_labels: # True if the dataset has labels
label = self.labels[index] return token_ids, attn_masks, token_type_ids, label else: return token_ids, attn_masks, token_type_ids
train = Data.DataLoader(dataset=MyDataset(sentences, labels), batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=1)# modelclass BertClassify(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BertClassify, self).__init__()
self.bert = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model, output_hidden_states=True, return_dict=True)
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, n_class) # 直接用cls向量接全连接层分类
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
def forward(self, X):
input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids = X[0], X[1], X[2]
outputs = self.bert(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids) # 返回一个output字典
# 用最后一层cls向量做分类
# outputs.pooler_output: [bs, hidden_size]
logits = self.linear(self.dropout(outputs.pooler_output))
return logits
bc = BertClassify().to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adam(bc.parameters(), lr=1e-3, weight_decay=1e-2)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()# trainsum_loss = 0total_step = len(train)for epoch in range(epoches): for i, batch in enumerate(train):
optimizer.zero_grad()
batch = tuple(p.to(device) for p in batch)
pred = bc([batch[0], batch[1], batch[2]])
loss = loss_fn(pred, batch[3])
sum_loss += loss.item()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step() if epoch % 10 == 0:
print('[{}|{}] step:{}/{} loss:{:.4f}'.format(epoch+1, epoches, i+1, total_step, loss.item()))
train_curve.append(sum_loss)
sum_loss = 0# testbc.eval()with torch.no_grad():
test_text = ['我不喜欢打篮球']
test = MyDataset(test_text, labels=None, with_labels=False)
x = test.__getitem__(0)
x = tuple(p.unsqueeze(0).to(device) for p in x)
pred = bc([x[0], x[1], x[2]])
pred = pred.data.max(dim=1, keepdim=True)[1] if pred[0][0] == 0:
print('消极') else:
print('积极')
pd.DataFrame(train_curve).plot() # loss曲线测试单条样本结果:
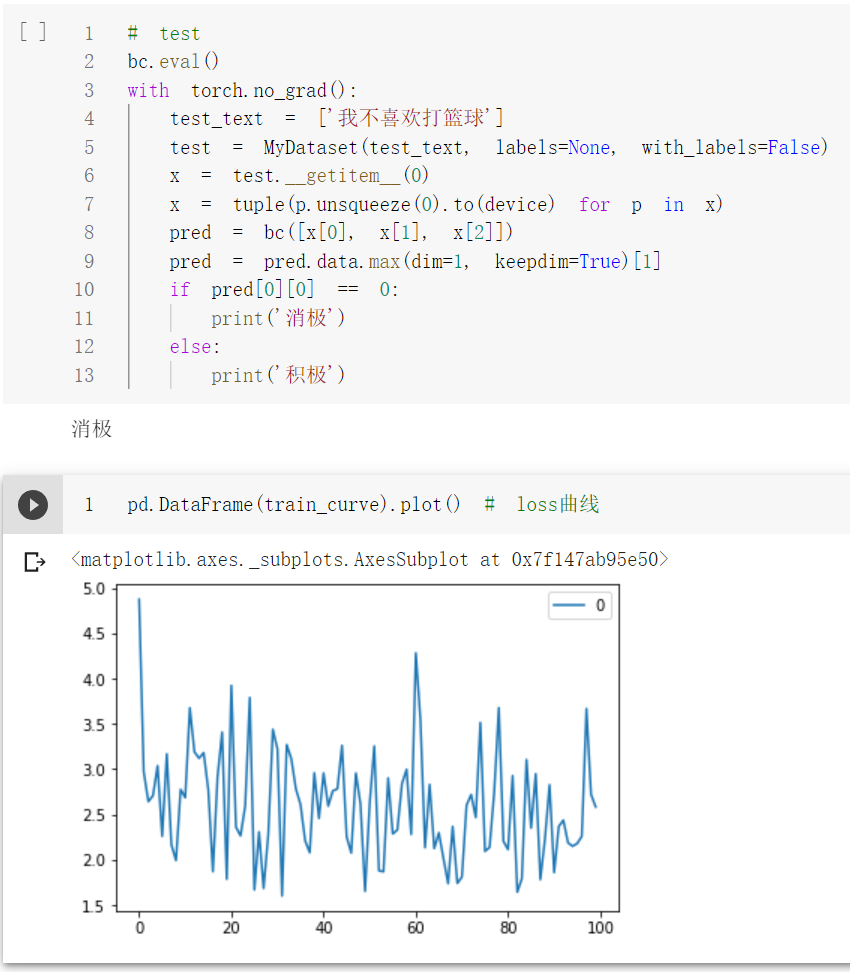
代码链接:
jupyter版本:https://github.com/PouringRain/blog_code/blob/main/nlp/bert_classify.ipynb
py版本:https://github.com/PouringRain/blog_code/blob/main/nlp/bert_classify.py
喜欢的话,给萌新的github仓库一颗小星星哦……^ _^
来源https://www.cnblogs.com/qingyao/p/15389307.html

